OUR PROJECT
At a Glance
People with diabetes have blood sugar (glucose) levels higher than normal, i.e., hyperglycemia. Diabetes is a very common disease.
Type 2 diabetes usually occurs in adulthood and is associated with overweight and lack of physical activity.
Hyperglycemia sustained for weeks and months can cause health complications, such as heart, kidney and eye diseases. People with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes tend to live fewer years.
Controlling high blood sugar in type 2 diabetes is achieved through a balanced diet, regular physical activity and, often, medication use. Diabetes is a chronic disease and therefore treatment is for life.
It is not always easy for people with type 2 diabetes to take care of themselves on a daily basis. It has been shown that less than half of the people type 2 diabetes achieve target levels for blood sugar, frequently because of difficulties in following recommendations about diet, physical activity and medication-taking. It is very important to help these people improving the way they care for themselves.
Several technological interventions have been studied in this respect. These interventions resort, for example, to text messages to mobile phones or websites. One of the advantages is that they can be automated, not depending on the availability of healthcare professionals; another advantage is convenience – they can be used anytime and without the need for people to move away from their homes.
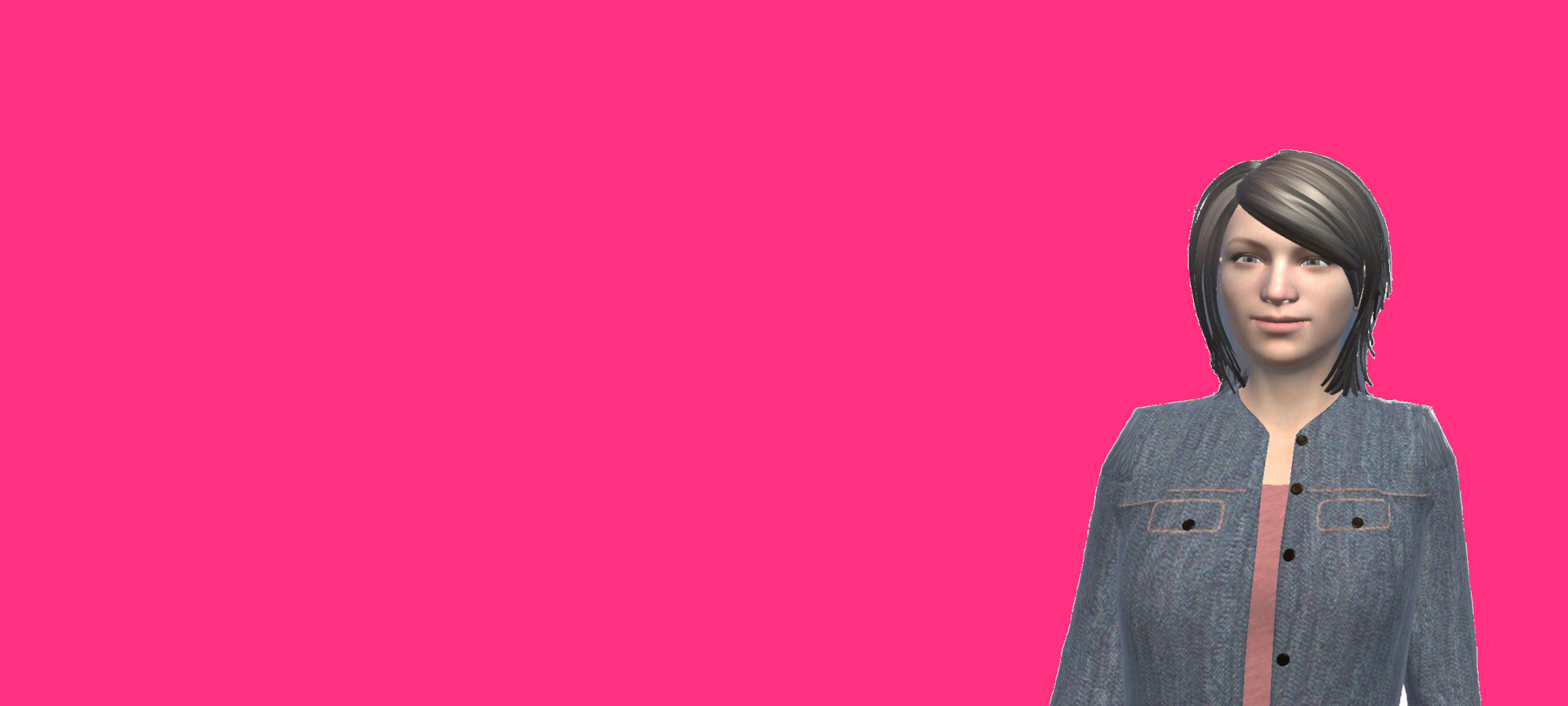
Virtual humans are computer artifacts researched and developed to assist people with chronic diseases to change and sustain self-care behaviours. These virtual assistants are designed to establish long-term relationship with users. They have shown good results in promoting health or controlling other chronic diseases, even in older people, less familiarised with technology.
Our Objective
The VASelfCare project aims to develop a viable prototype of a relational agent software to assist older adults with type 2 diabetes in self-care and to test its use in this group.
In this context, a prototype is a software in an early stage of development, used for testing purposes. The prototype forms the basis of potentially optimised versions.
Our Work Programme
VASelfCare pioneered the research and development of a human virtual assistant for older adults with type 2 diabetes, namely through state-of-the-art behaviour change science and usability principles for seniors.
The project was divided into two phases. In the first phase, the software was developed together with older people with type 2 diabetes, health professionals and other experts, as well as published scientific literature and clinical guidelines. Usability tests of the software were performed and adjustments made.
The second phase pertained to software testing over several months by older adults with type 2 diabetes.
Funding covered a period of 26 months, until March 2020; the project is currently in the sustainability and exploitation phase. Funding details can be found here.
Our Working Culture
Over the course of the project we built a cohesive team spirit and a set of procedures, unwritten rules and values about our approach to digital research and development.
We resort to coproduction with users to better meet their needs and optimise the benefits of digital technology.
We advocate students’ involvement in our project and believe it positively impacts education, research and technology.
We draw on the following core values:
- Interdisciplinarity. We recognise that innovation is supported by knowledge from different disciplinary domains and that looking at a problem with varied lenses may shift paradigms;
- Openness. We strive to create an environment where everyone is comfortable to share ideas, views and knowledge contributions;
- Responsibility. We honour our commitments with final users and to each other. We take ownership of our work and are willing to improve it whenever needed;
- Creativity. We look at challenges from different perspectives and embark on a lean approach to generate new solutions;
- Dynamism. We tackle tasks with a sense of strategy and accept that we will learn by doing;
- Proximity. We work closely with end-users and other relevant stakeholders to maximise value generation. We nurture a high-performance team by turning to each other when we need help.
Our Results
Project execution between 03-01-2018 to 05-03-2020 entailed as result indicator an innovative software prototype successfully tested. A second result indicator, not initially envisaged, was a prototype of a web-based dashboard for health professionals, populated by mobile application data.
During this period, the following performance indicators were met:
- 4 international papers published;
- 5 master theses concluded;
- 21 presentations in scientific events;
Check the resources tab for full details on project outputs.
Sustainability and exploitation look at opportunities of maximising the impact through the use of technology and knowledge created by the project. We hope that ultimately the prototype can be matured into a technological solution able to improve control of type 2 diabetes in older people, reducing disease progression and its consequences. The sustainability and exploitation phase includes the development of a web-based self-management education application with the virtual assistant Vitoria.
OUR PARTNERS
VASelfCare is an interdisciplinary consortium of four Higher Education Institutions, led by the Nursing School of Lisbon (ESEL). The consortium joined efforts with six Family Health Units of the Portuguese National Health Service to conduct research and help bridging the translational gap.
In addition to an interdisciplinary core team, about 50 graduate and undergraduate students from nursing, pharmacy, sport sciences and computer sciences have been involved, ranging from full-time to a few hours per week.
The team’s expertise ranges from behavior change theory and behaviour change techniques, clinical communication, medication adherence, physical activity in special populations, computer graphics and artificial intelligence to the development of digital health interventions.
- Escola Superior de Enfermagem de Lisboa
- Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa
- Faculdade de Farmácia da Universidade de Lisboa
- Instituto Politécnico de Santarém
The Escola Superior de Enfermagem de Lisboa (ESEL) is a public institution of higher education that actively seeks excellence and innovation in teaching and research in nursing. ESEL has about 1800 students, 1300 enrolled in the undergraduate nursing course and around 500 in postgraduate training (master's and other graduate programs). Since 2004, ESEL has maintained a partnership with the Universidade de Lisboa for a doctoral program in nursing. ESEL also has partnerships with several institutions in Europe and in Portuguese speaking countries, in addition to strong relationships with the community, through volunteering and other activities.
Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa (FCUL) is an education and research institution, which aims to promote the quality of the higher education and to develop competitive research units, both at a national and at an international level. With more than two hundred on-going projects, research activities at the FCUL are carried out in 20 Laboratories and Research Centres or Institutes embracing a variety of domains in Science and Technology, including Computer Sciences and Informatics. Many of these R&D activities are carried out in collaboration with international teams and are funded both at national and at European levels.
Faculdade de Farmácia da Universidade de Lisboa (FFUL) is a public higher education institution dedicated to education, research, knowledge transfer and university extension in the field of Pharmacy, Medicines and Pharmaceutical Sciences. With the motto "By knowledge, by innovation", FFUL is a recognised institution at the national and international level both in teaching and research. Scientific research in FFUL is ensured by the Research Institute for Medicines (iMed.ULisboa) which includes more than 200 researchers, concentrating its activity in four areas: Drug Discovery of therapeutic targets, Design of new molecules, Pharmaceutical Development and Rational use of Medicines (3DU).
Instituto Politécnico de Santarém (IPSantarém) is a public Portuguese Higher Education Institution with more than 35 years of experience in the fields of higher education and applied research. IPSantarém integrates five Schools and a Research Unit, including the School of Sports (ESDRM), located in Rio Maior. The School has a Sports Research Centre connected to the Research Unit of IPSantarém - including the areas of Physiology, Biomechanics, Motor Control, Sport Management, Sport Psychology and Sport Pedagogy. ESDRM staff is also involved in other research centres, supported by the National Foundation for Science & Technology.
Team members

Afonso Rodrigues
BSc Student
Maria Helena Batata

Sílvia Lopes
BSc StudentPast team members

Ana Isabel Pinto
MSc Student
Ana Raquel Santos
MSc StudentMariana Henriques
MSc Student | IUEM
António Dias
BSc Student
Diogo Marques
BSc StudentJoão Anastácio
MSc Student
Pedro Alves
MSc Student
Pedro Neves
MSc Student
Joshua Figueira
BSc StudentOUR RESOURCES
Communication & Dissemination
- All
- Book Chapter
- Conference Presentations
- Papers
- Newsletters
- Conference abstracts
- Theses

HCist
23rd October 2020

1ª Jornadas Enf. Com. ESEL
21st November 2019

48th ESCP Symposium
23rd - 25th October 2019

1º Congr. Intern. Literacia Saúde
16 - 17th May 2019
Check our social media!
Do not miss our YouTube content!
EVENTS
- All
- Workshops
- Tech Talks
- Physical activity sessions
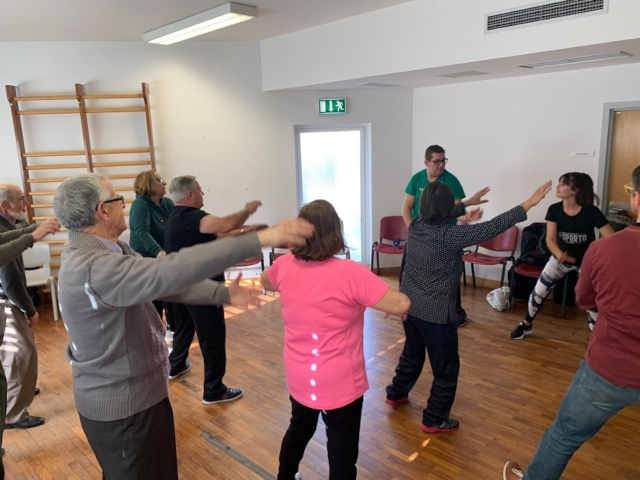

Physical activity sessions with older people
14th November 2019 | 2nd December 2019
STUDENTS
We are no longer accepting applications for research internships, course assignments or BSc/MSc theses in this project.








































